Online table redefinition allows you to restructure your Oracle® table in production without making the data unavailable. You might be comfortable using temp tables to move data around, but there is a better solution.
Introduction
Staging the data and moving it around while you restructure your table makes both the table and the data unavailable for a certain period, which is a less than favorable situation for businesses. This is when the
DBMS_REDEFINITION package saves the day, as shown in the following image: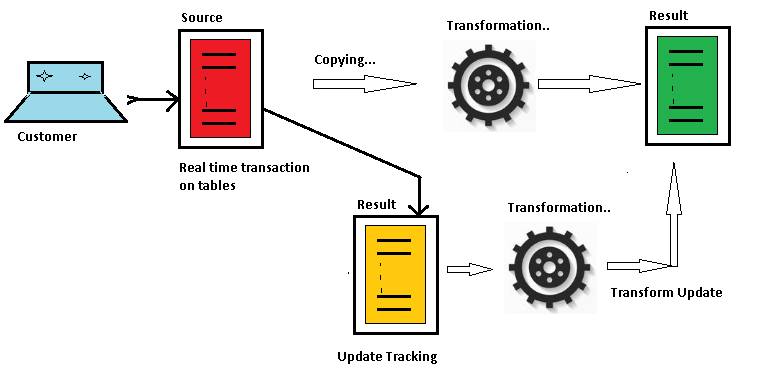
Purpose
Periodically, you need to modify the logical or physical structure of an Oracle table for the following reasons:
- To enhance queries or Data Manipulation Language (DML) performance
- To accommodate application changes
- To manage storage
Oracle Database provides a mechanism to make table structure modifications without significantly affecting the availability of the table, which is known as online table redefinition. Redefining tables online provides a substantial performance boost when compared to traditional methods of redefining tables.
When a table is redefined online, it is accessible to both queries and DML during most of the redefinition process. The table is locked in exclusive mode for only a short period, which is independent of the size of the table and the complexity of the redefinition. The redefinition process is completely transparent to users.
Online table redefinition requires free space that is approximately equivalent to the space currently used by the table being redefined.
There are numerous ways to reorganize a table. When downtime is a challenge, then the
DBMS_REDEFINITION package is the best option for this task.Redefine a table online
Use the following steps to redefine a table online.
- Choose the redefinition method, either
by keyorby rowids.
By key: Select a primary key or pseudo-primary key to use for the redefinition. Pseudo-primary keys are unique keys where all the component columns contain
NOT NULL constraints. For this method, the versions of the tables before and after redefinition should consist of the same primary key columns. This is the preferred and default method of redefinition.
By rowid: Use this method if no key is available. In this method, a hidden column, named
M_ROW$$, is added to the post-redefined version of the table. This column should be dropped or marked as unused after the redefinition is complete. If COMPATIBLE is set to 10.2.0 or higher, the final phase of redefinition automatically sets this column as unused. You can then use the ALTER TABLE ... DROP UNUSED COLUMNS statement to drop it. You cannot use this method on index-organized tables.- Verify that the table can be redefined online by invoking the
CAN_REDEF_TABLEprocedure. If the table is not a candidate for online redefinition, then this procedure raises an error indicating why the table cannot be redefined online. - Create an empty interim table (in the same schema as the table to be redefined) with all of the desired logical and physical attributes.
- It is not necessary to create the interim table with all the indexes, constraints, grants, and triggers of the table being redefined. This can be done automatically by using the
COPY_TABLE_DEPENDENTSprocedure. - To improve performance in larger tables, you can set it in parallel by using the following commands:
- The
FINISH_REDEF_TABLEcommand completes the redefinition of the table. During this procedure, the original table is locked in an exclusive mode for a short time, independent of the amount of data in the original table. However,FINISH_REDEF_TABLEwaits for all the pending DML operations to commit before completing the redefinition. - If you used
rowidsfor the redefinition and yourCOMPATIBLEinitialization parameter is set to 10.1.0 or lower, you need to drop the hidden columnM_ROW$$that was added to the redefined table. You can also set the column to "UNUSED" by using the following command:
If
COMPATIBLE is 10.2.0 or higher, this hidden column is automatically set to UNUSED when the redefinition completes. You can then drop the column with the ALTER TABLE ... DROP UNUSED COLUMNS statement. Wait for any long-running queries against the interim table to complete and then drop the interim table.Sample table redefinition
The following section shows examples of the various commands and outputs for a sample table redefinition.
START SQLPLUS
The following sample demonstrates starting
sqlplus:CREATE A DEMO TABLE
The following sample demonstrates creating a demo table name
TEST1 under AMIT schema.INSERT BULK ROWS
The following sample demonstrates inserting bulk rows and setting
PPA_AGGGREGATE_TARGET in AMIT schema to max value.CREATE DEPENDENT OBJECTS FOR TESTING
The following sample demonstrates creating dependent objects related to table
TEST1 rows, so that you can see what happens during an online redefinition.
View creation
Sequence creation
Procedure creation
DML trigger creation
Primary key creation
Get the status before redefinition
CHECK TABLE FOR REDEFINITION
The following sample demonstrates checking that the table can be redefined online using either
rowids or primary key:
Using primary key
Using rowid
CREATE A REPLICA OF THE INTERIM TABLE
The following sample demonstrates creating a replica of new interim table without any dependent objects:
CONNECT TO DATABASE
The following sample demonstrates connecting by using a privilege user to execute the table redefinition task:
START REDEFINITION
The following sample demonstrates starting redefinition by using a primary key:
COPY DEPENDENT OBJECTS
The following sample demonstrates automatically copying dependent objects like mview, primary key, view, sequence, and triggers.
IGNORE_ERROR is set to TRUE to avoid primary key violation with the COPY_TABLE_DEPENDENTS command.CHECK FOR ERRORS
The following sample demonstrates checking for errors in
DBA_REDEFINITION_ERRORS view:VALIDATE BOTH TABLES
The following sample demonstrates validating the row count on both tables and syncing with the interim table:
FINISH THE REDEFINITION
The following sample demonstrates finishing the redefinition:
CHECK ERROR AND RECOMPILE THE SCHEMA
The following sample demonstrates recompiling the schema with complete dependency, which is necessary because of the invalid triggers in the preceding step:
DROP THE INTERIM TABLE
The following sample demonstrates dropping the interim table:
Conclusion
If a table structure needs to be modified and simultaneously accessed by end users, use
DBMS_REFDEFINITION.
This feature helps reorganize the data without any downtime, thus avoiding challenges caused by downtime for customers in an online transaction processing (OLTP) environment.
Authentic content..very knowledgble.. thanks for this post..
ReplyDeleteIntroduction To Tally
Versions Of Tally
Excellent idea!!! I really enjoyed reading your post. Thank you for your efforts. Share more like this
ReplyDeleteRobot Framework
Test Framework